Treble and Bass Clef Notes: The Essential Guide to Sheet Music
Intro
Reading sheet music with treble and bass clef notes is an essential skill for any musician. I learned early on that knowing how to read these notes correctly allowed me to interpret musical pieces accurately, as well as compose and play my own songs. In this guide, I will discuss how to read treble and bass clef notes, as well as provide some helpful tips on how to practice reading them. We’ll also look at how the notes are used in various musical genres and provide resources to help you hone your skills. By the end of this guide, you should have a firm grasp of treble and bass clef notes and be able to read sheet music.
Understanding the Basics of Treble and Bass Clef Notation
When it comes to reading sheet music, one of the fundamental skills you need to acquire is the ability to read treble and bass clef notes. These clefs are used to notate the different ranges of pitches in music, and being able to read them correctly is essential for any musician.
The treble clef, also known as the G clef, is commonly used to notate higher-pitched instruments such as the violin, flute, and piano’s right hand. It consists of a stylized “G” shape that wraps around the second line of the staff. The notes on the lines and spaces of the treble clef staff represent higher pitches, starting with the E below middle C.
On the other hand, the bass clef, also known as the F clef, is used for lower-pitched instruments like the cello, double bass, and piano’s left hand. It is marked by two dots that surround the fourth line of the staff. The notes on the lines and spaces of the bass clef staff represent lower pitches, starting with the G below middle C.
To fully understand treble and bass clef notation, it’s important to be familiar with the scales associated with each clef. The treble clef scale spans from the F below middle C to the G above the staff. On the other hand, the bass clef scale extends from the E below the staff to the G above the staff.
By memorizing the positions of the notes on each clef, you’ll be able to identify and read them quickly and accurately. It may take some practice at first, but with time and patience, you’ll become more comfortable with reading both treble and bass clef notes.
In the next sections of this guide, I will dive deeper into each clef and explore how to read their respective notes. I will also discuss how to read notes in both clefs simultaneously, as well as key signatures and time signatures in sheet music.

The Treble Clef Staff and Its Notes
The Treble Clef Staff is a crucial element of reading sheet music with treble and bass clef notes. It is primarily used to notate higher-pitched instruments such as the violin, flute, and the right hand of the piano. Understanding how to read the notes on the treble clef staff is essential for any musician.
The treble clef staff consists of five lines and four spaces. The lines, from bottom to top, represent the notes E, G, B, D, and F, while the spaces represent the notes F, A, C, and E. The notes on the lines and spaces of the treble clef staff represent higher pitches, starting with the E below middle C.
To memorize the positions of the notes on the treble clef staff, it can be helpful to use mnemonic devices. For example, many musicians remember the lines on the treble clef staff by using the mnemonic “Every Good Boy Does Fine,” where each letter represents the first letter of the note on each line. Similarly, the spaces on the treble clef staff can be remembered using the mnemonic “F-A-C-E.”
In addition to the notes on the lines and spaces, it’s important to be familiar with the treble clef scale. The treble clef scale spans from the F below middle C to the G above the staff. By understanding the range of pitches represented on the treble clef staff, you’ll be able to read and interpret the music accurately.
As you practice reading notes on the treble clef staff, it can be helpful to start with simple exercises and gradually increase the difficulty level. There are also many online resources and apps available that can provide practice materials and quizzes to help you improve your skills.
By mastering the treble clef staff and its notes, you’ll be able to confidently read and play music written for higher-pitched instruments. Remember to take your time, practice regularly, and don’t be afraid to ask for help or seek additional resources when needed. With dedication and persistence, you’ll soon become proficient in reading treble clef notes.


The Bass Clef Staff and Its Notes
The Bass Clef Staff is just as important as the Treble Clef Staff when it comes to reading sheet music with treble and bass clef notes. It is primarily used to notate lower-pitched instruments such as the cello, double bass, and the left hand of the piano. Understanding how to read the notes on the bass clef staff is essential for any musician.
Similar to the treble clef staff, the bass clef staff consists of five lines and four spaces. The lines, from bottom to top, represent the notes G, B, D, F, and A, while the spaces represent the notes A, C, E, and G. The notes on the lines and spaces of the bass clef staff represent lower pitches, starting with the G below middle C.
To help remember the positions of the notes on the bass clef staff, you can use mnemonic devices just like with the treble clef staff. For example, you can use the phrase “Good Boys Deserve Fudge Always” to remember the notes on the lines, with each word representing the first letter of the note on each line. For the spaces, you can use the phrase “All Cows Eat Grass” to remember the notes on the spaces.
In addition to the notes on the lines and spaces, it’s important to be familiar with the bass clef scale. The bass clef scale extends from the E below the staff to the G above the staff. By understanding the range of pitches represented on the bass clef staff, you’ll be able to read and interpret the music accurately.
As you practice reading notes on the bass clef staff, it’s helpful to start with simple exercises and gradually increase the difficulty level. You can also find online resources and apps that provide practice materials and quizzes to help you improve your skills.
By mastering the bass clef staff and its notes, you’ll be able to confidently read and play music written for lower-pitched instruments. Remember to practice regularly, be patient with yourself, and seek out additional resources if needed. With dedication and perseverance, you’ll soon become proficient in reading bass clef notes.
So far, we have discussed the basics of treble and bass clef notation and explored how to read the notes on the treble clef staff and the bass clef staff. In the next section of this guide, we will dive into the topic of reading notes in both clefs simultaneously. Stay tuned for more valuable insights and tips to enhance your sheet music reading skills!
How to Read Notes in Both Clefs Simultaneously
Reading notes in both the treble and bass clefs simultaneously can seem like a daunting task at first, but with practice and perseverance, it can become second nature. This skill is especially important for musicians who play instruments that require both clefs, such as the piano.
To read notes in both clefs simultaneously, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of each clef individually. Start by practicing reading notes in one clef until you feel comfortable and confident. Then, gradually introduce the other clef and begin to read notes from both clefs together.
One effective technique is to mentally associate the notes in each clef with their corresponding positions on the piano keyboard. For example, when you see a note on the treble clef, visualize its position on the right-hand side of the piano keyboard. Similarly, when you see a note on the bass clef, imagine its location on the left-hand side of the keyboard. This mental connection can help you quickly identify the notes in each clef while reading sheet music.
Another helpful strategy is to practice sight-reading exercises that incorporate both clefs. Start with simple pieces and gradually increase the difficulty level as you become more comfortable. Focus on maintaining a steady tempo and rhythm while transitioning between the treble and bass clefs. As you progress, you’ll find that your reading speed and accuracy improve.
Additionally, it’s essential to understand how the notes in each clef relate to each other. Take note of any patterns or intervals between the notes in both clefs. This knowledge can assist you in recognizing common chord progressions and melodic phrases.
Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering the skill of reading notes in both clefs simultaneously. Dedicate time each day to practice sight-reading exercises and gradually challenge yourself with more complex musical pieces. With patience and perseverance, you’ll soon find yourself effortlessly reading notes in both the treble and bass clefs, unlocking a whole new level of musical expression.
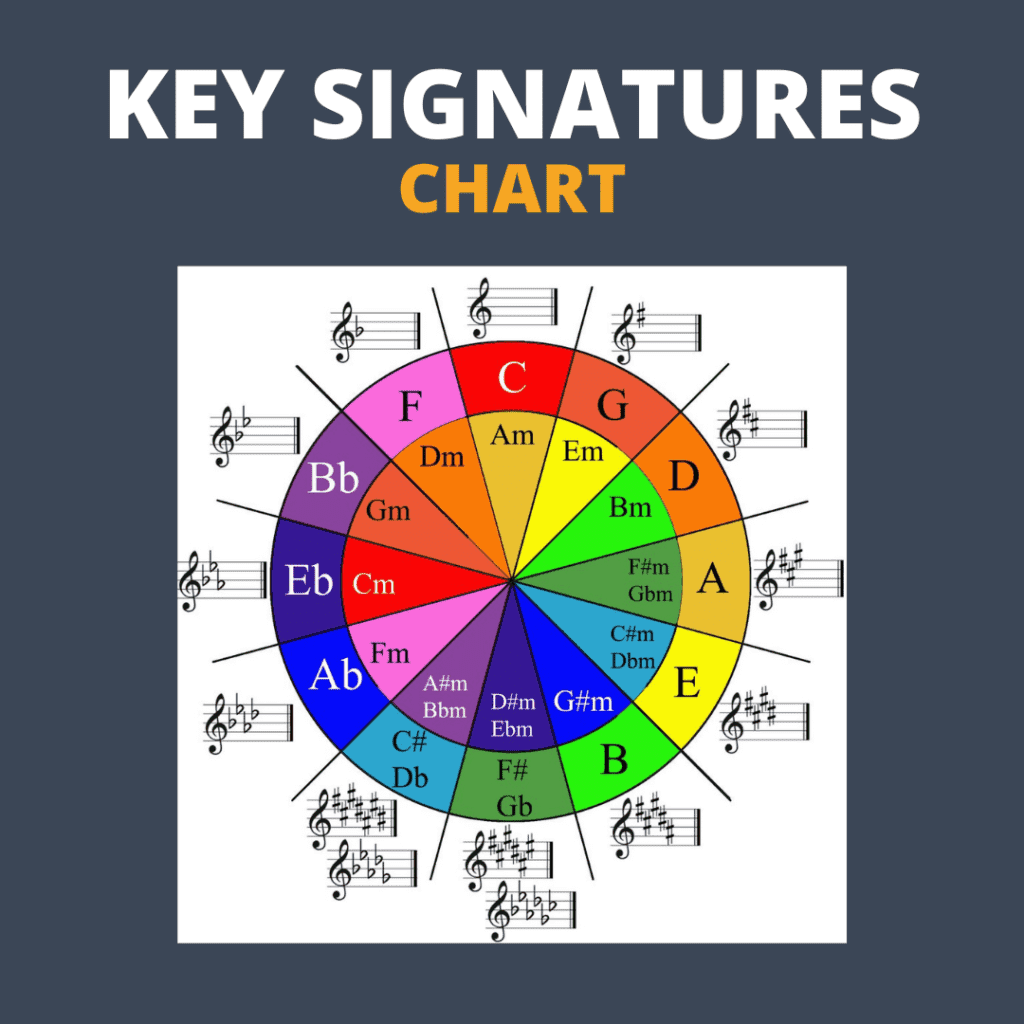
Key Signatures and Time Signatures in Sheet Music
Key signatures and time signatures are important elements of sheet music that provide crucial information about the musical piece.
Key signatures indicate the key of the music, which determines the notes and chords that will be used throughout the piece. They are typically found at the beginning of each staff and consist of sharps (#) or flats (b) placed on specific lines or spaces. Key signatures help musicians quickly identify the tonality of the music and play the correct notes. For example, a piece in the key of G major will have an F# in its key signature, indicating that all F notes should be played as F# throughout the piece.
Time signatures, on the other hand, indicate the rhythm and time signature of the music. They are typically represented by two numbers stacked on top of each other, such as 4/4 or 3/4. The top number indicates the number of beats per measure, while the bottom number indicates the note value that receives one beat. For example, in a 4/4 time signature, there are four beats per measure, and the quarter note receives one beat. Time signatures provide musicians with a framework for counting and interpreting the rhythm of the music.
Understanding key signatures and time signatures is crucial for accurately interpreting and performing a musical piece. It allows musicians to play the correct notes and maintain the proper rhythm. It’s important to take the time to study and familiarize yourself with different key signatures and time signatures, as they can vary greatly between musical pieces and genres.
One way to practice key signatures and time signatures is to study and analyze different musical compositions. Take note of the key signatures and time signatures used and try to identify patterns and relationships between them. Additionally, you can use online resources and apps that provide exercises and quizzes to help you practice identifying key signatures and time signatures.
Mastering key signatures and time signatures takes time and practice, but it is a crucial step in becoming a proficient musician. By developing a strong understanding of these elements, you’ll be able to read and interpret sheet music with ease and accuracy. So keep practicing, and soon you’ll be confidently playing and composing music using the correct key signatures and time signatures.
Conclusion
Tips and Tricks for Mastering Treble and Bass Clef Reading
Reading treble and bass clef notes can be challenging, but with some tips and tricks, you can master this essential skill. Here are some strategies to help you improve your treble and bass clef reading:
1. Practice regularly: Like any skill, reading sheet music requires practice. Set aside dedicated time each day to work on reading treble and bass clef notes. Consistency is key, so make it a habit to practice regularly.
2. Start with simple exercises: Begin by practicing with simple exercises that focus on individual notes and gradually increase the difficulty level. This will help you build a strong foundation and gradually improve your reading skills.
3. Use mnemonic devices: Mnemonic devices can be a helpful tool to remember the notes on each clef. For example, you can use phrases like “Every Good Boy Does Fine” for the lines on the treble clef and “Good Boys Deserve Fudge Always” for the lines on the bass clef. Similarly, the spaces on the treble clef can be remembered with the phrase “F-A-C-E” and the spaces on the bass clef with “All Cows Eat Grass.”
4. Focus on patterns and intervals: Take note of patterns and intervals between the notes in both clefs. This knowledge can help you recognize common chord progressions and melodic phrases, making it easier to read and interpret sheet music.
5. Practice sight-reading: Sight-reading exercises are a great way to improve your reading skills. Start with simple pieces and gradually increase the difficulty level. Focus on maintaining a steady tempo and rhythm while transitioning between the treble and bass clefs.
6. Use online resources and apps: There are numerous online resources and apps available that can provide practice materials and quizzes to help you improve your treble and bass clef reading. Take advantage of these tools to enhance your skills and track your progress.
7. Seek guidance and feedback: If you’re struggling to improve on your own, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a music teacher or mentor. They can provide valuable feedback and offer personalized tips to help you overcome any challenges you may be facing.
Remember, mastering treble and bass clef reading takes time and patience. Stay dedicated to your practice, and soon you’ll be able to read sheet music with ease and confidence. Now get to practicing!




